Mapping Privacy Controls to GRC Programs
Privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS are pushing organizations to rethink how they manage sensitive data. But privacy isn’t just about compliance—it’s about building trust and managing risk.
One of the most effective ways to operationalize privacy is by embedding privacy controls directly into your Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework.
In this post, we’ll walk through how to map key privacy requirements into your existing GRC policies, processes, and tools to streamline compliance and strengthen accountability.
Why Privacy Controls Belong in GRC
Your GRC program already governs:
- Policies and standards
- Risk management
- Control testing
- Audit response
- Regulatory tracking
By aligning privacy controls with these components, you create a single source of truth for both data protection and compliance, reducing gaps and duplication.
This approach helps:
- Ensure privacy risks are tracked alongside other business risks
- Make audits smoother and faster
- Prove due diligence to regulators and customers
- Operationalize data protection at scale
Key Privacy Control Categories to Integrate
| Privacy Domain | Control Examples | Where to Map in GRC |
|---|---|---|
| Data Inventory | Identify, classify, and map personal data across systems | Risk Register, Asset Management, Data Governance Policy |
| Access Management | Enforce role-based access, least privilege, logging | Access Control Policy, Identity Risk Assessment |
| Data Minimization | Limit collection and retention of PII | Privacy Policy, Retention Schedule, Data Lifecycle Controls |
| Consent Management | Capture, log, and enforce data subject consent | Privacy Controls, Legal Register*, Vendor Assessments |
| Incident Response | Include data breach notification procedures | Incident Response Plan, Business Continuity Playbook |
| Third-Party Risk | Validate vendor privacy practices and contracts | Vendor Risk Management, TPRM Workflow, Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) |
A Legal Register in GRC refers to a centralized record of legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations, including regional privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA. It ensures compliance requirements are tracked, assigned, and updated.
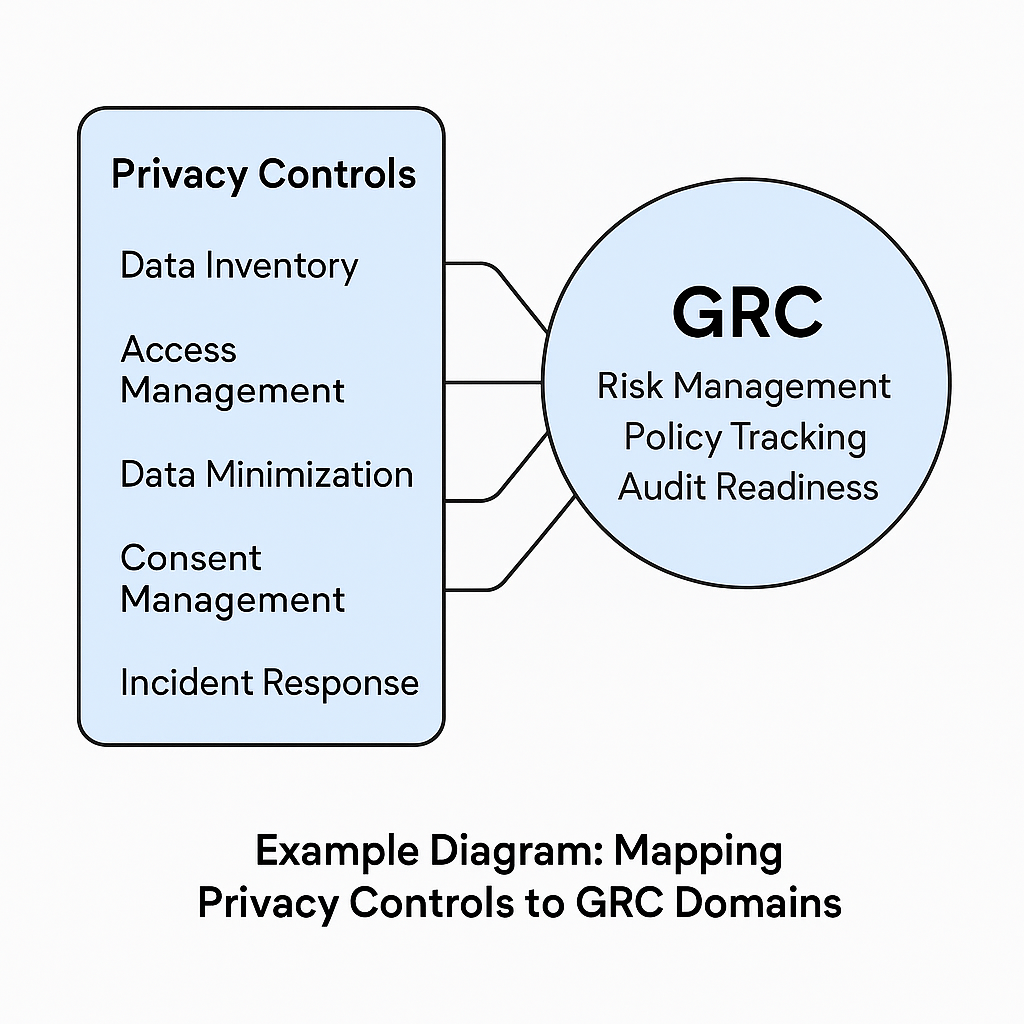 Figure: Visualizing how privacy domains align with common GRC processes like risk management, policy tracking, and audit readiness.
Figure: Visualizing how privacy domains align with common GRC processes like risk management, policy tracking, and audit readiness.
6 Steps to Map Privacy Controls to GRC
1. Inventory Privacy Requirements
Gather privacy obligations from:
- GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, etc.
- Industry-specific mandates
- Contractual privacy clauses
Document these as control objectives in your GRC platform or spreadsheet.
Popular Tools to Explore:
Organizations can use tools like OneTrust, LogicGate, Archer, or TrustArc to manage control libraries, privacy registers, and risk tracking. Even lightweight platforms like Tugboat Logic or Confluence-based templates can help smaller teams build scalable processes.
2. Map to Existing Policies and Controls
Look at what you already have:
- Does your Access Control Policy reference PII?
- Do you have a retention schedule?
- Are breach procedures documented?
For each privacy requirement, link it to a policy, control, or evidence source in your GRC system.
3. Use Your Risk Register to Track Privacy Risks
Add risks such as:
- “Unauthorized access to PII”
- “Lack of encryption at rest”
- “Non-compliance with DSAR timelines”
Map these to appropriate controls and risk owners. Prioritize based on likelihood and impact.
4. Align Testing & Audit Activities
Update your internal control testing plan to include:
- Privacy notice review
- Consent tracking accuracy
- Vendor DPA verification
- Access control audits tied to PII systems
This makes privacy auditable, testable, and reportable.
5. Automate Where Possible
Use GRC tools or scripts to:
- Track DSR (Data Subject Request) fulfillment time
- Monitor data retention violations
- Validate vendor privacy certifications
Automation improves compliance confidence and efficiency.
6. Train Stakeholders Across Departments
Privacy controls aren’t just for IT. Train:
- HR on employee data handling
- Marketing on consent and email practices
- Procurement on vendor privacy due diligence
Use your GRC awareness program to deliver role-based training tied to privacy responsibilities.
Common Challenges When Integrating Privacy into GRC
Mapping privacy controls into your GRC program isn’t always smooth. Common obstacles include:
- Siloed data ownership across departments
- Limited internal resources for documentation and maintenance
- Resistance to change from non-technical teams
- Tool fatigue or lack of centralized systems
Tips to Overcome Them:
- Start small with one or two privacy domains (e.g., access control + retention).
- Use cross-functional champions to bridge privacy, legal, and security.
- Automate evidence collection and workflow notifications when possible.
Final Thoughts
Privacy isn’t a siloed function. It’s a core part of governance, risk, and compliance.
By embedding privacy controls directly into your GRC framework, you can:
- Simplify audits
- Increase organizational accountability
- Meet global regulations more effectively
- Build customer and stakeholder trust
Privacy isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about building a defensible, transparent, and ethical business.